This article was originally published on Techcrunch.com on July 22, 2020. This article is part 3 of a 3 part series about selling company stock. Written by Peyton Carr.
In a recent article, I covered all of the reasons you might be tempted to hold a highly-concentrated position in your company stock as a tech founder and how it fits into your portfolio. I then followed up with a rundown on why resisting diversification is generally a bad idea and the subconscious biases that hold us back from selling.
So now that you understand the benefits of diversification and have taken inventory of your portfolio, what is the most effective way for you to move forward? I will share with you what to keep in mind before selling, how to decide when to sell, and strategies to execute sales such as options, exchange funds, prepaid variable forward contracts, qualified small business stock, and tax considerations. Now, let’s take a deep dive into strategic approaches to take as a shareholder and important tax implications to consider.
Keep in Mind: Lockups and Blackout Periods
Most tech companies that IPO have a 180-day lockup period that prevents insiders, employees, and VC funds from selling immediately. There is usually language that also prohibits hedging with derivatives (options) during that period. Lockups are intended to help prevent insider trading and provide the company with additional post-IPO price stability.
It is also important to abide by the company’s blackout periods, which prohibit transactions during more share-price-sensitive times, such as earnings or material non-public information releases.
Concentrated Stock Strategies
Ad-hoc Selling
This is the most straightforward and involves the outright sale of your shares. However, this can be difficult for various reasons such as selling restrictions, the perception by others that you are unloading stock, and many psychological biases that act as internal mental obstacles.
Scheduled Selling
Selling all your stock at once could be both emotionally challenging and tax-inefficient. Scheduled selling involves the selling of a set number of shares over a specific period. This selling strategy can help by spreading the tax impact over a few years. It also provides an advantage from a psychological standpoint since the plan is determined upfront, then mechanically executed.
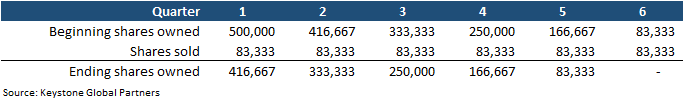
As an example, a founder might plan to sell 500,000 shares over 18 months. The founder is comfortable selling quarterly, which equals six selling periods of 83,333 shares per quarter. In a scenario where a founder is subject to blackout periods, a 10b5-1 trading plan can be implemented and set on autopilot. The company may even allow you to sell your shares during blackout periods with a 10b5-1 trading plan. See the example of scheduled selling below.
Hedging with Options
Multiple hedging strategies can be implemented to protect your downside; however, some of the more common approaches used are the protective put and the protective collar. Below are basic examples of how these strategies are executed, for illustrative purposes.
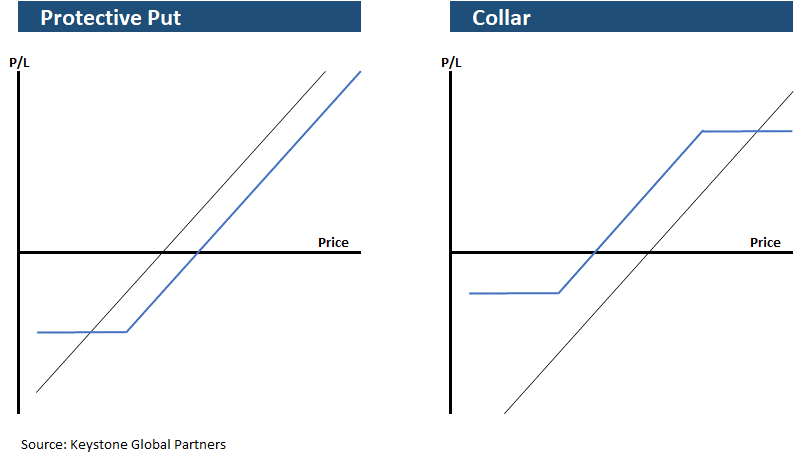
Protective Put– Buying protection against the downside
Collar – Give up some upside, to limit some downside
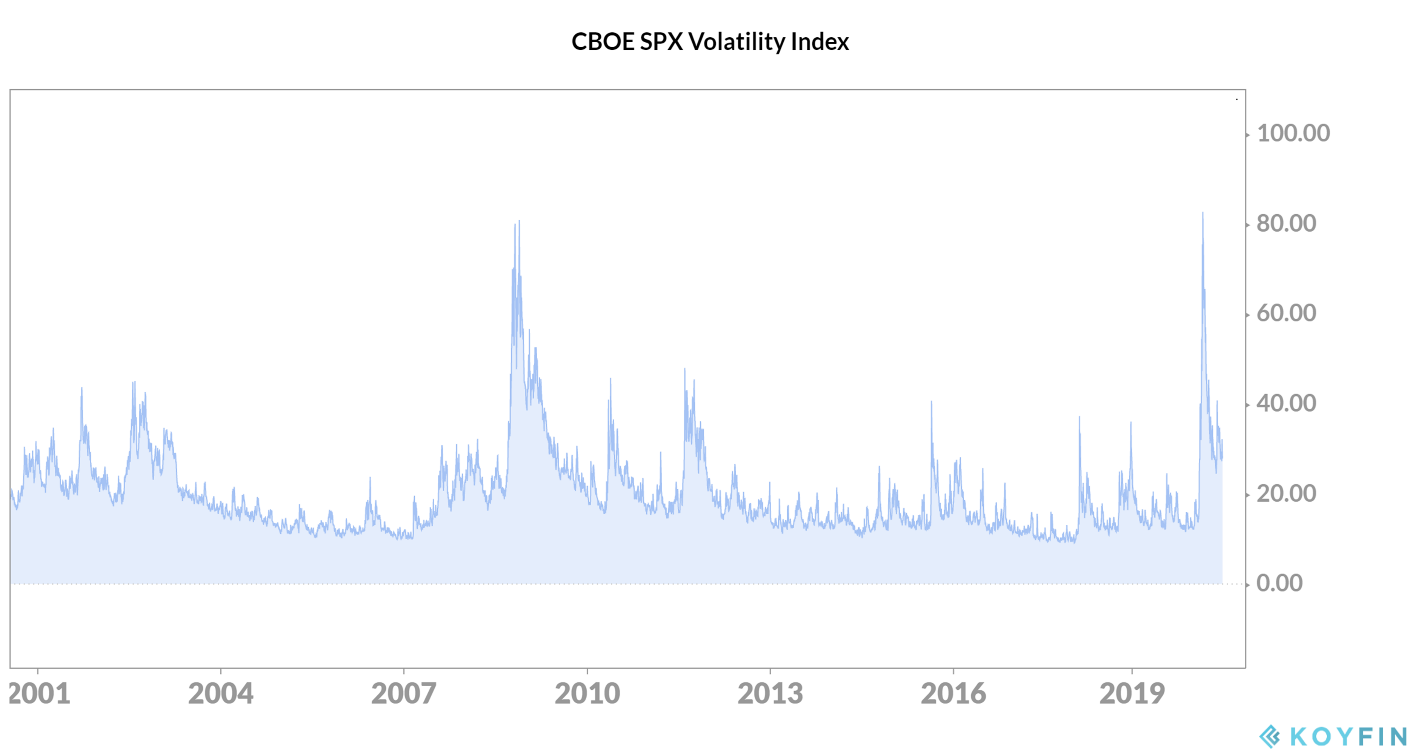
Each strategy allows the owner to continue holding the stock while providing some downside protection against a stock’s decline. However, these strategies are not tax-efficient and are complicated, so working with an expert is essential. Both puts and certain types of collars would have been extremely expensive to implement during the recent market crisis because market volatility is a factor in options prices. See the below chart of the VIX (volatility index) during peak crisis. However, in some instances, these strategies can make sense.
Exchange Funds
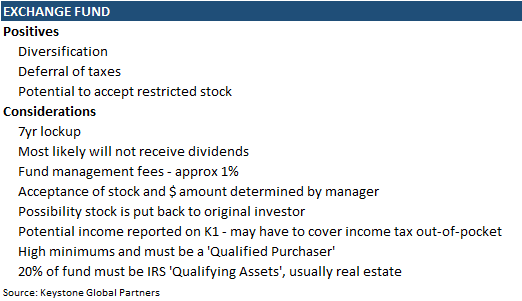
This strategy allows an investor to contribute their concentrated stock position into an exchange fund partnership alongside other investors who also contribute their stock positions. In return, each investor receives a diversified stock portfolio, selected by an investment manager. This strategy allows the investor to achieve immediate diversification while deferring the taxes that they would have otherwise paid in most situations.
At the end, usually seven or more years out, each investor receives a basket of stocks. They pay zero tax if they hold the stocks forever, but if you sell, your aggregate cost basis is equal to the cost basis of the original shares contributed. Some downsides of using exchange funds to consider are lockups, expenses, and sometimes not achieving the desired level of diversification. Below I detail some high-level positives and considerations.
Prepaid Variable Forward Contract
This strategy enables a shareholder to synthetically diversify their equity exposure by entering into an agreement (contract) with a bank or brokerage firm to receive a loan now, and sell their stock at a future date. The reason it is ‘variable’ is because the amount of stock the shareholder delivers in the future depends on share value upon expiration. The shareholder can also decide in the future to cash-settle (deliver cash) instead of delivering (selling) stock.
This strategy is essentially a combination of a type of equity collar, described in the options section above, and a loan. Because this is an option, pricing varies based on market conditions and the stock involved. If structured correctly, the shareholder does not pay tax until the future sale date.
Fun fact is, recently, it was disclosed in an SEC filing that Vince McMahon had entered one of these covering approximately 3.5 million shares, or $80 million of WWE stock. Many perceived this as him effectively selling about 15% of his shares and questioned whether he was ready to “tap out” for good.
Below is a hypothetical example of a prepaid variable forward.

When Should You Sell IPO Stock?
Based on an analysis of 258 IPOs, it is usually the most beneficial for shareholders to sell their stock as soon as possible after the lockup period expires. If you look at the performance of holding IPO stocks for the long term versus selling immediately and diversifying, the results may surprise you.
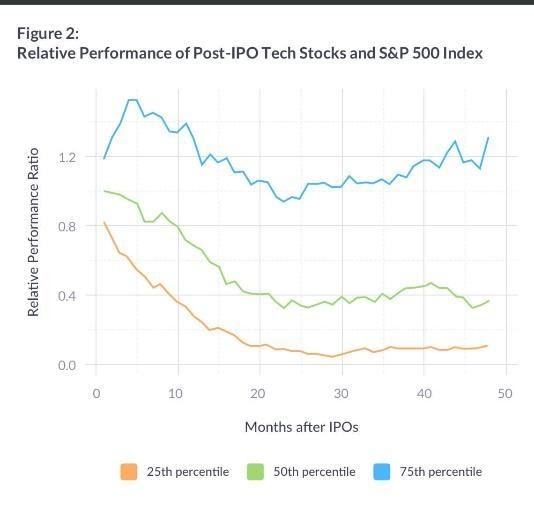
This chart shows a sample of 258 IPOs from 1990 to 2012, and the four years following their lockup expiration. The data illustrates that the median tech IPO underperforms the S&P 500 index by around 20% after the first year following lockup expiration. Even the best IPOs that fall into the top quartile, still barely keep up with the S&P 500. You must be very confident that your company is an exception to this.
These findings are also consistent with the underperformance of IPO stocks relative to the S&P 500, as reported by Professor Jay Ritter, an academic authority on IPOs. If you’d like to dig deeper like I do, you can download his full data set here.
Consider Taxes Before You Sell
When deciding to sell, it’s important to consider taxes. We realize that concentrated stock often comes with a very low cost basis, which can be another obstacle for investors to overcome before selling.
How you own your stock and how long you have owned it will ultimately determine how you are taxed. Below is a chart showing the different types of taxation on various forms of equity compensation.
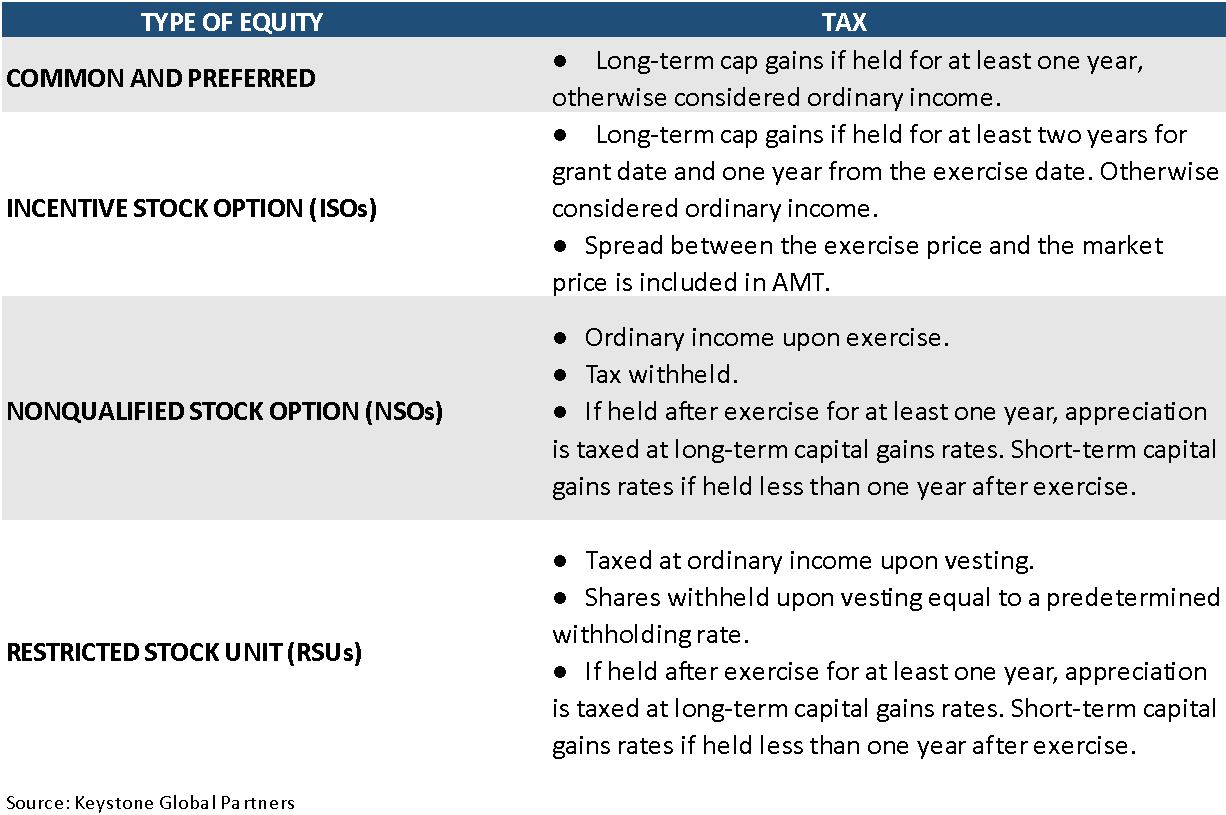
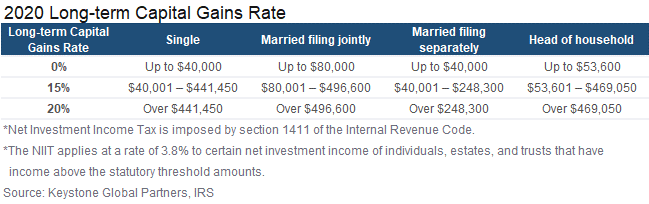
Two important things to consider are whether you will be taxed at long-term or short-term capital gains rates and whether you qualify for the qualified small business stock (QSBS) exclusion. Your income will impact the rates at which you are taxed. Please consult with your advisor before making any decisions.
Generally, we suggest making investment decisions and then optimizing for tax. I always tell my clients not to let the tax tail wag the investment dog. However, there are scenarios where it can make sense to hold your stock for slightly longer to minimize taxes owed.
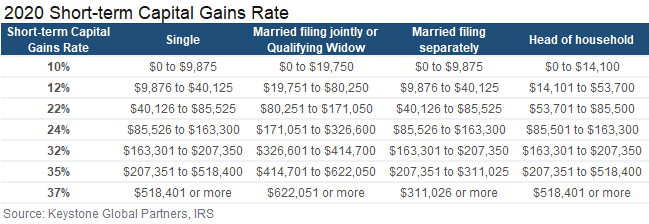
For example, short-term capital gains (holding period < 1 year) can be far more expensive than paying taxes on a long-term capital gain (holding period > 1 year).
Let’s say you own $1 million of XYZ, a $100 stock, with one month to go before it qualifies for long-term capital gains treatment. In the example below, if the stock maintains the same price for the next month, you can net 27% more in after-tax profits; you get to keep an extra $170,000. Even if the stock price drops 21%, you would still net the same profits as if you had sold it at the previous higher price but subject to the higher short-term capital gains rate. See the example below.
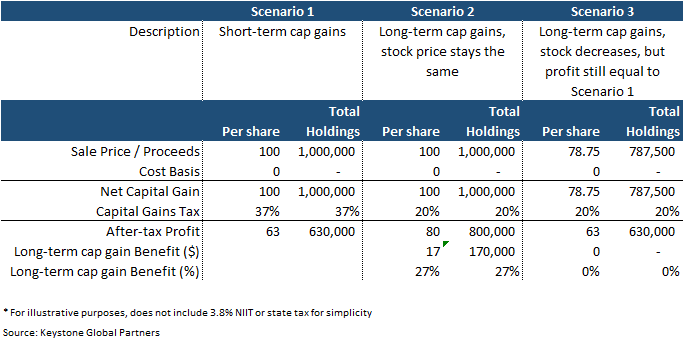
Careful planning is required, as IPOs can have very volatile share prices. If XYZ sells off significantly over the next month, it is possible you can be in a far worse scenario than having just sold it outright and paying the short-term capital gains. Nobody has a crystal ball, but understanding the tradeoffs is helpful in the decision-making process.
Qualified Small Business Stock (QSBS)
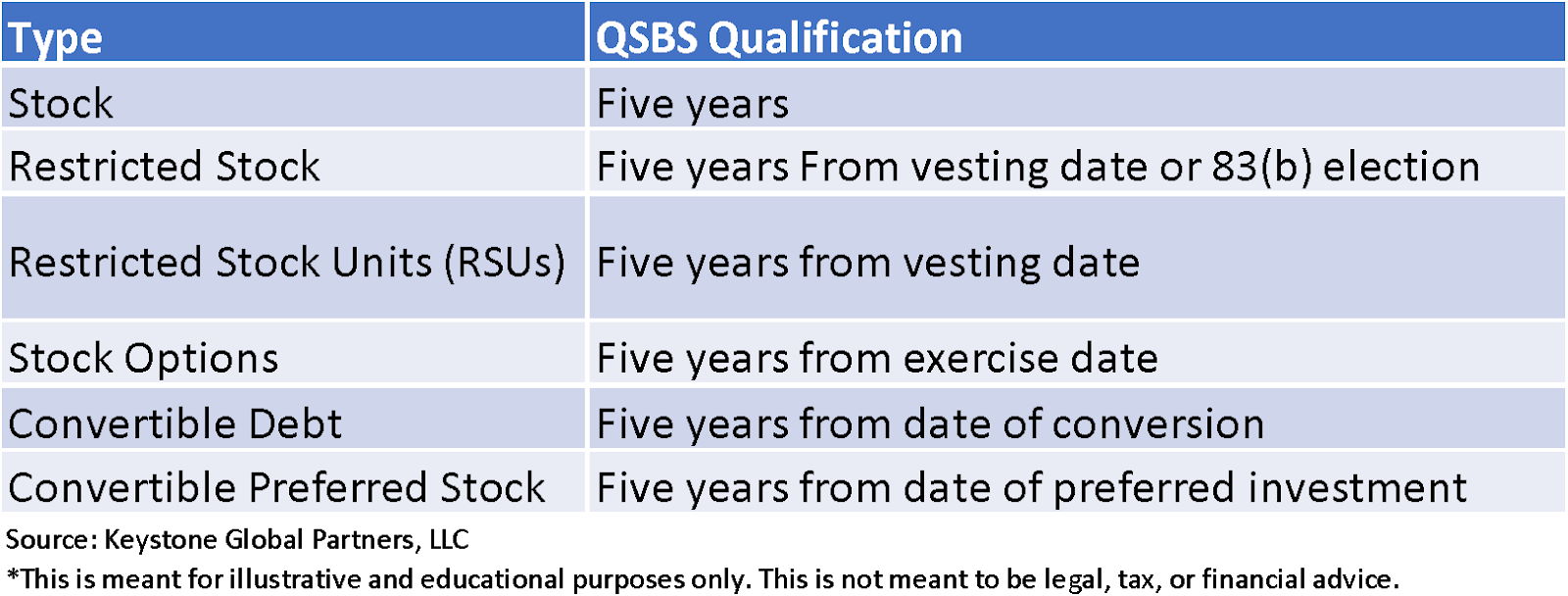
If your shares qualify for the QSBS exclusion, you could potentially sidestep up to 100% of your capital gains taxes upon sale. That is not a typo, this is arguably one of the most significant tax opportunities out there. If you are a founder or early employee and you have held your shares for over five years, this is something you should look into.
You can reference the table below to determine the QSBS qualification holding period for different types of equity. This is one of the most valuable and significant tax incentives for founders and early employees, but not everyone will qualify.
Some further clarification on determining whether or not your shares qualify is below. For a more in-depth discussion on QSBS, you can reference the guide I wrote.
- Your company is a Domestic C Corporation.
- Stock is acquired directly from the company.
- Stock has been held for over five years.
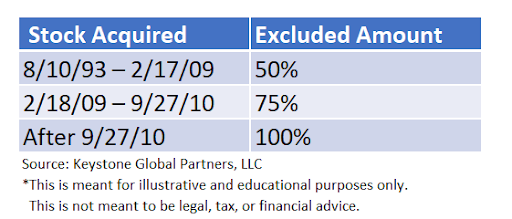
- Stock was issued after August 10th, 1993, and ideally, after September 27th, 2010, for a full 100% exclusion.
- Aggregate gross assets of the company must have been $50 million or less when the stock was acquired.
- The business must be active, with 80% of its assets being used to run the business. It cannot be an investment entity.
- The business cannot be an excluded business type such as, but not limited to: finance, professional services, mining/natural resources, hotels/restaurants, farming, or any other business where the business reputation is a skill of one or more of the employees.
Deciding whether or not to sell your company stock or when to sell it, is not a decision to enter into lightly. Rather than simply cashing in your stock for a quick payday or holding it in a highly concentrated position, dreaming of a potentially huge payday in the future, I encourage you to look deeper — at your big-picture financial goals, your overall investment portfolio, details and strategies specific to employee shareholders, and important tax implications. A rational, evidence-based approach will produce the best path forward.
Want to learn how to handle your stake in company stock with a sharp focus on achieving your personal financial goals? Download our In-Depth Guide, The Founder’s Guide to Managing Your IPO Stock.
Disclaimer
The information and opinions provided in this material are for general informational purposes only and should not be considered as tax, financial, investment, or legal advice. The information is not intended to replace professional advice from qualified professionals in your jurisdiction.
Tax laws and regulations are complex and subject to change, and their application can vary widely based on the specific facts and circumstances involved. Any tax information or advice in this article is not intended to be, and should not be, used as a substitute for specific tax advice from a qualified tax professional.
Investment advice in this article is based on the general principles of finance and investing and may not be suitable for all individuals or circumstances. Investments can go up or down in value, and there is always the potential of losing money when you invest. Before making any investment decisions, you should consult with a qualified financial professional who is familiar with your individual financial situation, objectives, and risk tolerance.
